How is Technology Being Used to Explore the Depths of the Ocean?
The ocean covers more than 70% of the Earth's surface, yet it remains one of the least explored regions on the planet. However, with the advancements in technology, scientists are now able to explore the depths of the ocean in ways that were once thought impossible.
One of the most important technological advancements in ocean exploration is the development of submersibles. These underwater vehicles are equipped with cameras and sensors that allow scientists to observe and collect data on the ocean's inhabitants and geology. Submersibles can reach depths of up to 36,000 feet, allowing scientists to explore the deep sea, where sunlight cannot reach.
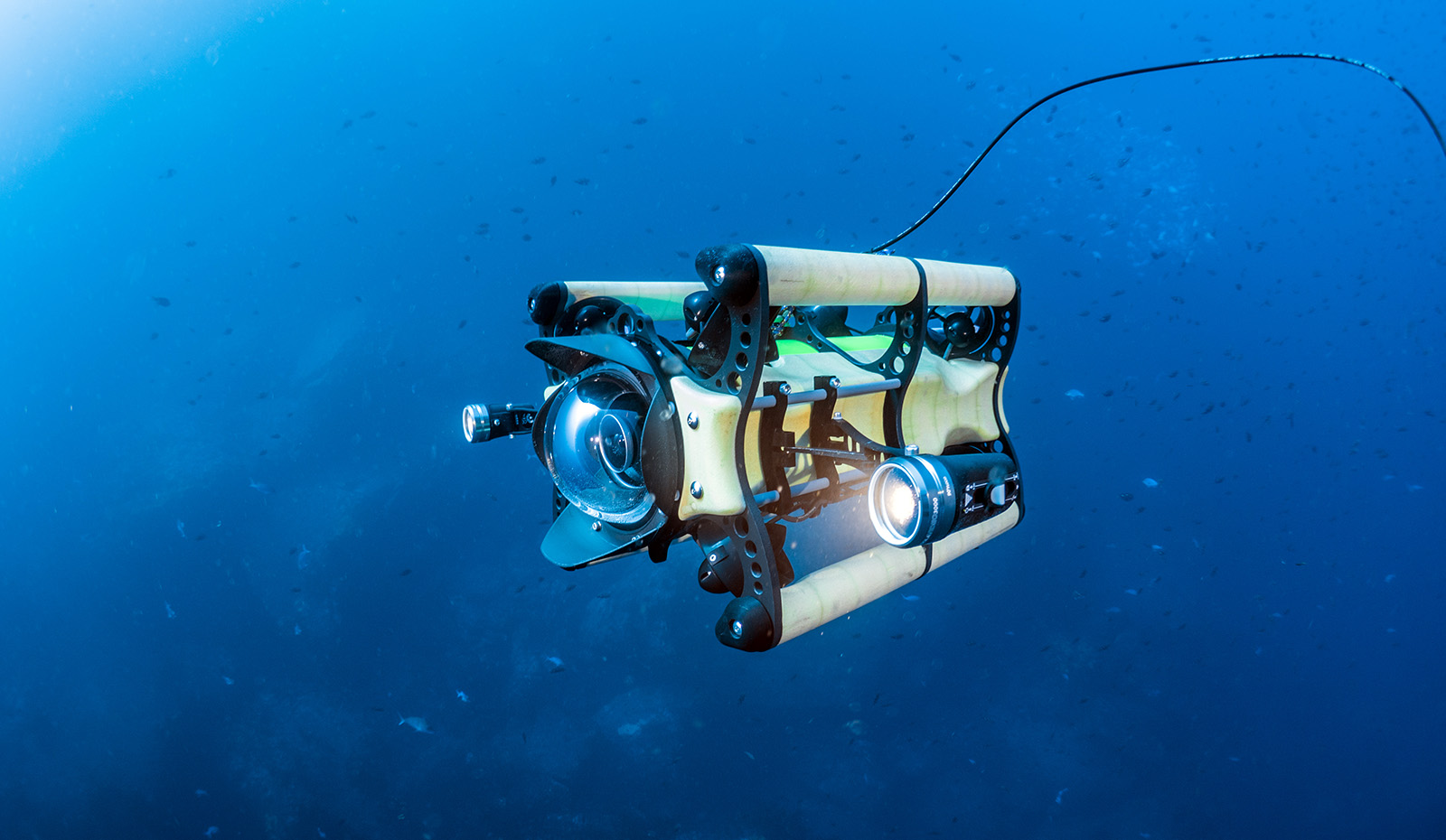
Another important technology used in ocean exploration is remotely operated vehicles (ROVs). ROVs are unmanned submersibles that are controlled remotely from the surface. They are equipped with cameras, lights, and manipulator arms that allow scientists to collect samples and perform other tasks without risking human lives. ROVs have been used to explore shipwrecks, study deep-sea habitats, and even map the ocean floor.
Satellite technology is also playing an important role in ocean exploration. Satellites equipped with high-resolution cameras can capture images of the ocean surface, providing scientists with valuable information about ocean currents, temperature, and the distribution of marine life. These images can also be used to detect and track oil spills and other environmental hazards.
In addition, autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are becoming more common in ocean exploration. These vehicles are self-propelled and can navigate and collect data on their own. They are equipped with a variety of sensors and can be programmed to explore specific areas of the ocean floor, track specific species, or collect samples at different depths.
Overall, technology is playing an increasingly important role in the exploration of the ocean. With the use of submersibles, ROVs, satellites and AUVs, scientists are able to explore the depths of the ocean and study marine life and geology in ways that were once thought impossible. This technology is helping us to better understand the ocean and its role in the Earth's ecosystem, and also, it has a great potential for many practical applications such as the discovery of new resources, marine conservation, and oceanography.